Integrating a Malware Sandbox into SOAR Workflows: Steps, Benefits, and Impact
SOAR platforms are excellent at moving work forward. They trigger playbooks, route incidents, and enforce consistent response steps. What they don’t do well on their own is confirm what’s actually SOAR helps teams move faster, but speed isn’t the real problem.
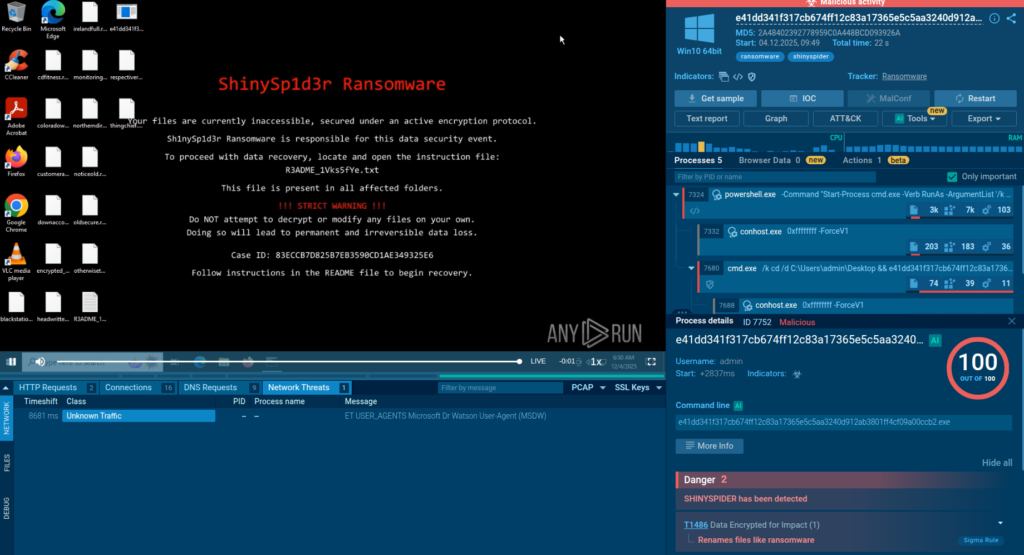
The real issue is figuring out what an alert actually means. A sandbox solves that by safely running the file or link and showing what it really does. With clear evidence in hand, playbooks make better decisions, triage moves quicker, and fewer incidents turn into long investigations.
Let’s walk through how teams use a sandbox inside SOAR, and what that means for faster decisions and lower risk.
Why a Sandbox Changes SOAR Outcomes
SOAR platforms are excellent at moving work forward. They trigger playbooks, route incidents, and enforce consistent response steps. What they don’t do well on their own is confirm what’s actually happening.
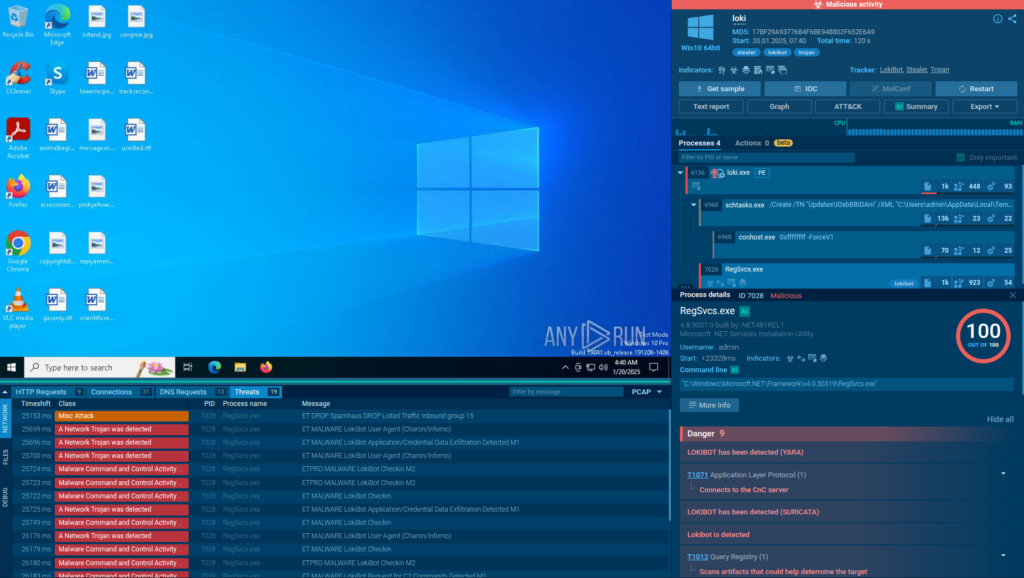
That gap matters. When alerts arrive with limited context, automation can only go so far. Teams hesitate, escalations increase, and playbooks stall while someone manually checks files, links, or indicators across multiple tools.
A sandbox changes this dynamic by adding behavior-based proof directly into the workflow. Instead of relying on assumptions or partial signals, SOAR receives concrete answers: what executed, what connected out, what dropped, and how risky it really is.
With that clarity:
- Triage decisions happen faster
- Playbooks trigger with more confidence
- Fewer cases get escalated “just in case”
In practice, SOAR stops being a traffic controller and starts acting like a decision engine; one that’s backed by real evidence, not guesses.
What a Sandbox Does Inside SOAR Workflows
When integrated into SOAR, ANY.RUN’s sandbox covers a few critical steps that static tools alone can’t reliably handle:
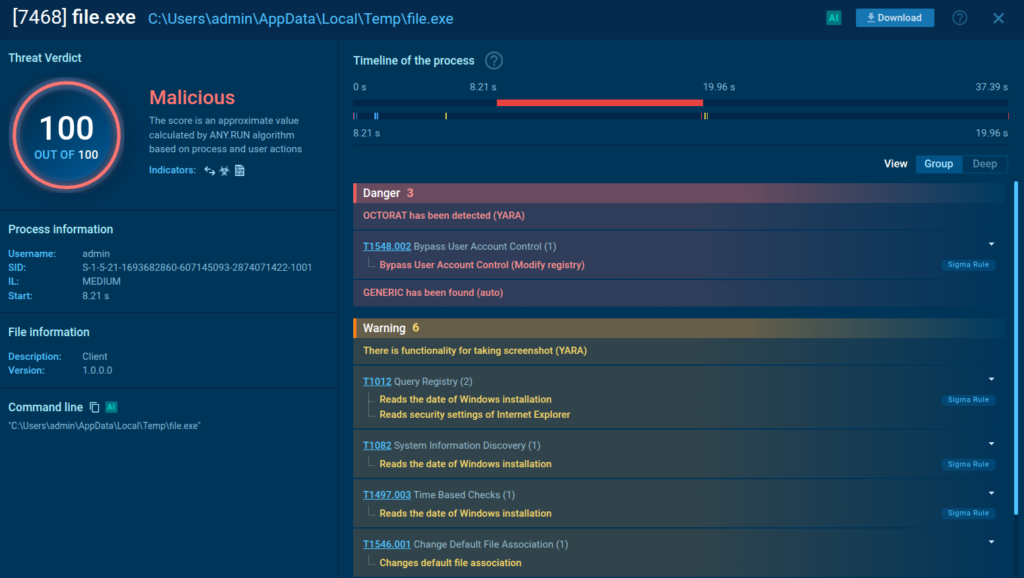
- Validates alerts with real behavior: Suspicious files and links are executed in a safe environment to confirm whether they’re actually malicious. This replaces guesswork with evidence early in the workflow.
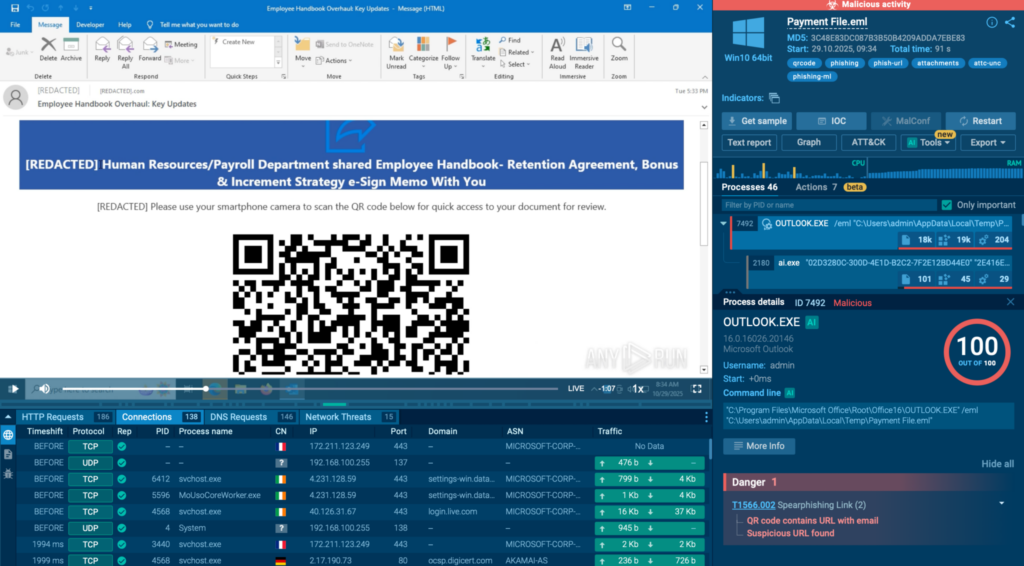
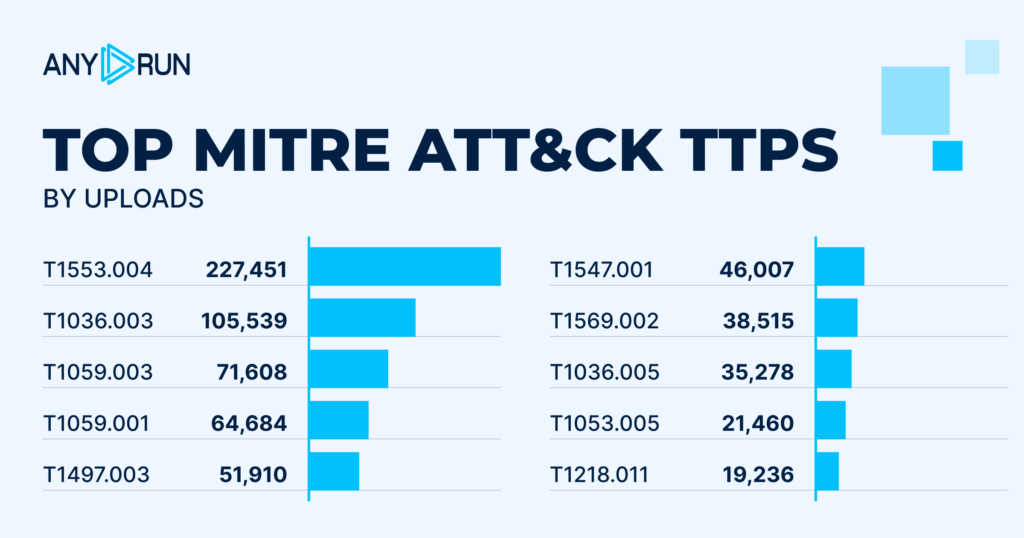
- Uncovers multi-stage and evasive attacks: Many threats reveal their intent only after redirects, downloads, or user interaction. A sandbox follows the full execution chain so SOAR can act on what truly happens, not what appears safe at first glance.
- Returns decision-ready context to playbooks: SOAR receives clear verdicts, risk scores, and indicators tied to observed behavior, giving playbooks the confidence to move forward without manual checks.
- Reduces unnecessary escalations: With reliable evidence available upfront, fewer cases are passed up the chain “just in case,” keeping response focused and queues under control.
- Enables safer automation: Once behavior is confirmed, SOAR can trigger containment, enrichment, and documentation steps with much lower risk of false positives.
Together, these capabilities allow SOAR workflows to run with more confidence and consistency, even during alert spikes, and without increasing operational overhead.
Where Sandbox-Driven SOAR Fits in Real Security Stacks
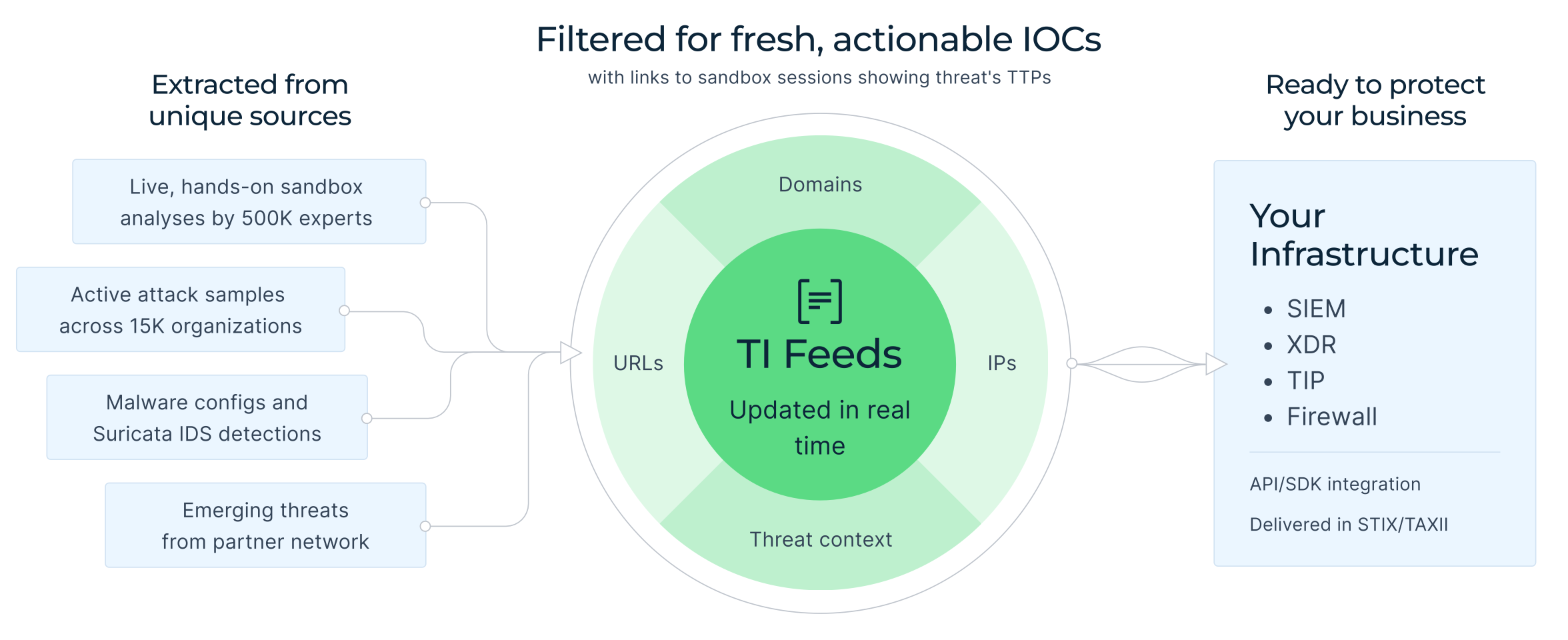
In enterprise environments, SOAR operates across SIEM, endpoint, and threat intelligence platforms. A sandbox fits into this layer as the system that validates behavior and feeds trusted context back into automation.
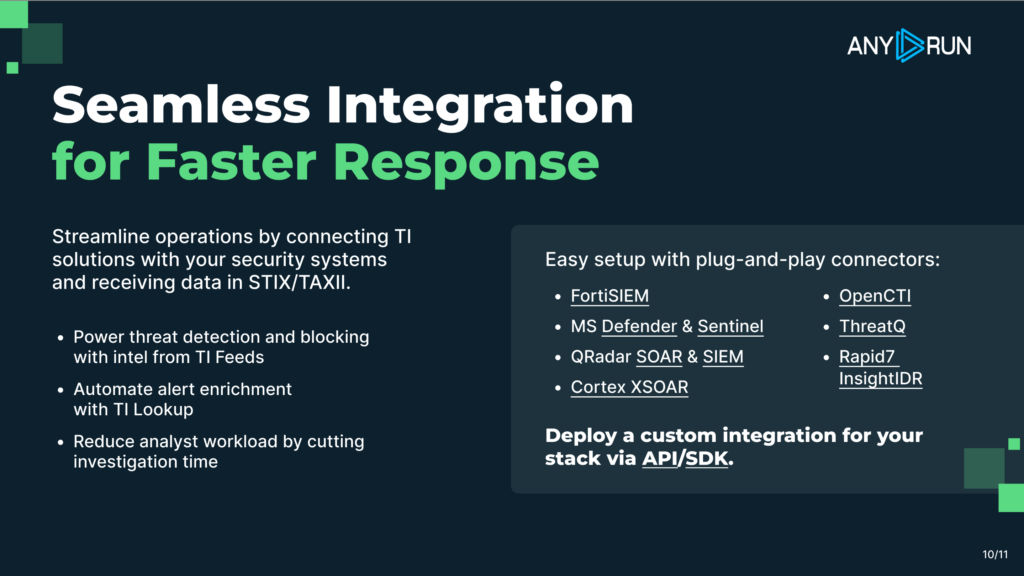
That’s why Interactive Sandbox integrations and connectors are designed to work directly inside widely used SOAR and security platforms, including:
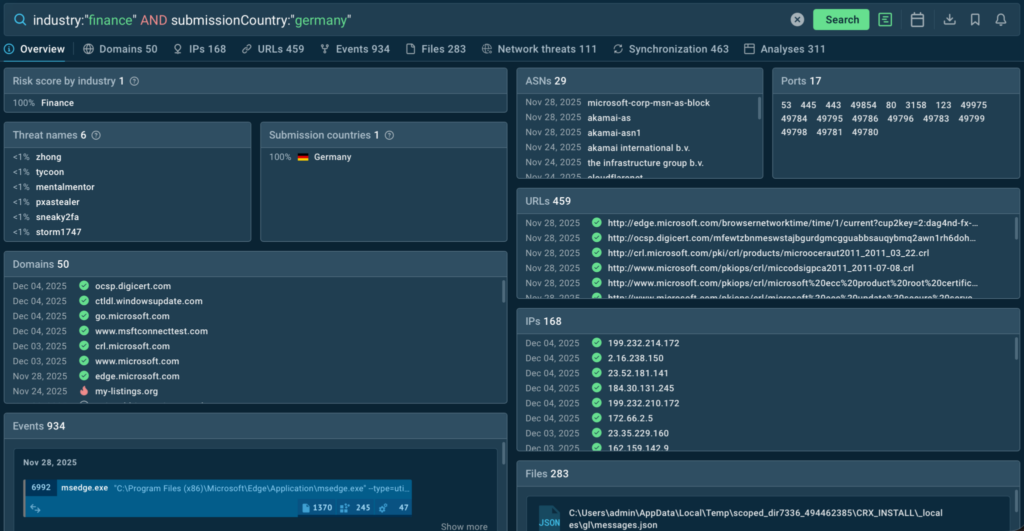
Within these environments, sandbox execution is triggered automatically from incidents or alerts. Files, URLs, and artifacts are analyzed in a safe environment, and the results, verdicts, risk scores, indicators, and behavioral context, are returned directly into the SOAR case.
This means teams don’t have to switch tools to understand what’s happening. Automation continues with confidence, response actions are triggered earlier, and threat intelligence is enriched as part of the same workflow.
Sandbox-driven SOAR is embedded into the platforms large organizations rely on today, making it easier to scale response without adding operational complexity.
From Faster Triage to Lower Risk: The Business Impact of Sandbox-Driven SOAR
When ANY.RUN’s sandbox is embedded into SOAR workflows, the impact goes beyond faster investigations. It changes how incidents are prioritized, handled, and closed with measurable effects at both the SOC and business level.
- Real-time threat visibility: Observe full attack chains as they unfold, with 90% of malicious activity exposed within the first 60 seconds, significantly accelerating mean time to detect (MTTD).
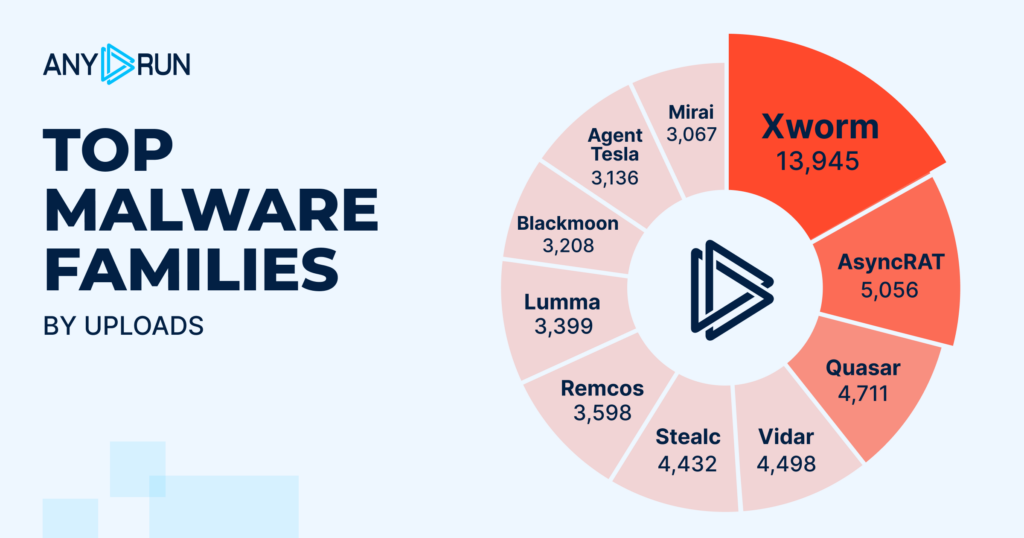
- Higher detection rates for evasive threats: Sandbox execution uncovers low-detection attacks, including multi-stage malware and interaction-dependent phishing, resulting in up to 58% more threats identified and fewer missed incidents.
- Lower MTTR across common incidents: With behavior confirmation available early, response steps trigger sooner and manual verification is removed from first-line playbooks, consistently shortening response cycles.
- Operational efficiency at scale: Automated sandbox execution reduces manual analysis time, cutting Tier 1 workload by up to 20% and allowing less experienced team members to handle more complex cases with confidence.
- Stronger performance during alert spikes: Evidence-driven automation keeps workflows stable during phishing waves or malware campaigns, helping teams avoid backlog growth and burnout.
- Clear business-level impact: Faster containment reduces the risk of lateral movement, data loss, and downtime, while automation lowers the cost per incident by minimizing repeated manual effort.
Turning Sandbox-Driven SOAR into a Scalable Security Strategy
SOAR works best when automation is backed by proof. By adding a sandbox into the workflow, teams replace uncertainty with clear behavior, shorten response cycles, and keep decisions consistent even under pressure.
With ready-made integrations across common SOAR and security platforms, sandbox-driven workflows fit naturally into existing stacks. The result is faster response, lower operational load, and reduced business risk, without expanding teams or tools.
See how sandbox-driven SOAR fits into your environment. Explore ANY.RUN’s Enterprise integrations and unified security workflows.
About ANY.RUN
ANY.RUN helps security teams make faster, clearer decisions when it matters most. The platform is trusted by over 500,000 security professionals and 15,000+ organizations across industries where response speed and accuracy are critical.
ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox allows teams to safely execute suspicious files and links, observe real behavior in real time, and confirm threats before they escalate. Combined with Threat Intelligence Lookup and Threat Intelligence Feeds, it adds the context needed to prioritize alerts, reduce uncertainty, and stop advanced attacks earlier in the response cycle.
Start a 2-week ANY.RUN trial →
SOAR moves tickets fast but can’t tell you what’s really happening. Malware sandbox gives you the proof: what ran, what connected out, what files dropped. Your playbooks turn into decision engines instead of waiting on manual checks.
Connectors trigger malware sandbox on alerts. You send files or URLs. Results come back fast. Verdicts, risk scores, IOCs, TTPs. Playbooks use that to triage, contain, or close without humans jumping in.
Multi-stage phishing and evasive malware. Malware sandbox follows redirects and downloads to show the full chain. Static scans miss this stuff.
Yes. Tier 1 gets clear evidence upfront. They close 70% more cases without passing them up. No more “just in case” handoffs.
For ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox, 90% of malicious behavior shows up in 60 seconds. Your playbooks act right away.
FortiSOAR, Cortex XSOAR, Splunk SOAR, Microsoft Sentinel, IBM QRadar SOAR, Google SecOps, and more.
Grab a 2-week trial. Pick your connector. Test it on real alerts. See the difference yourself.
The post Integrating a Malware Sandbox into SOAR Workflows: Steps, Benefits, and Impact appeared first on ANY.RUN’s Cybersecurity Blog.
ANY.RUN’s Cybersecurity Blog – Read More