Lazarus Group Attacks in 2025: Here’s Everything SOC Teams Need to Know
The Lazarus Group, North Korea’s state-sponsored hacking collective, has held the title of the most notorious advanced persistent threat (APT) for almost two decades now. In 2025, it escalated its cyber operations, targeting tech industries with fake IT workers, fraudulent job interviews, and hijacked open-source software.
It’s time to take a closer look at its current activities and see how SOC teams can proactively detect and track the group attacks using ANY.RUN’s solutions.
Biggest Lazarus Group Campaigns So Far
Lazarus’s 2025 campaigns combine sophisticated social engineering and supply chain attacks, posing severe risks to businesses’ financial stability, data security, and operational continuity.
North Korean IT Workers
Since 2024, Lazarus Group has been deploying North Korean operatives posing as legitimate remote IT workers to infiltrate companies, particularly in the U.S. and UK. Using stolen or AI-enhanced identities, these operatives secure tech roles to steal sensitive data, deploy malware, or generate illicit revenue for North Korea.
According to the U.S. Department of Justice, these schemes compromised over 100 U.S. companies, including Fortune 500 firms. For example, an Atlanta-based blockchain company lost over $900,000 in virtual currency due to insider access by fake IT workers.
Beyond financial losses, businesses face reputational damage, loss of intellectual property, and regulatory scrutiny for hiring vulnerabilities. Extortion attempts, where operatives hold stolen data hostage, further disrupt operations and erode customer trust.
Operation 99: Fake Job Interviews (Contagious Interview)
Operation 99 (aka “Contagious Interview”) is a campaign from Lazarus and its subgroups like Famous Chollima that targets tech, crypto developers and CEOs, with fake job and partnership interviews.
Posing as recruiters on LinkedIn, Telegram, or Calendly, Lazarus lures victims with fraudulent coding tests hosted on malicious GitLab repositories. As part of the scheme, Lazarus hackers utilize NPM packages.
For C-suite targets, criminals typically share fake Zoom executables and malware disguised as other software widely used in corporate environments.
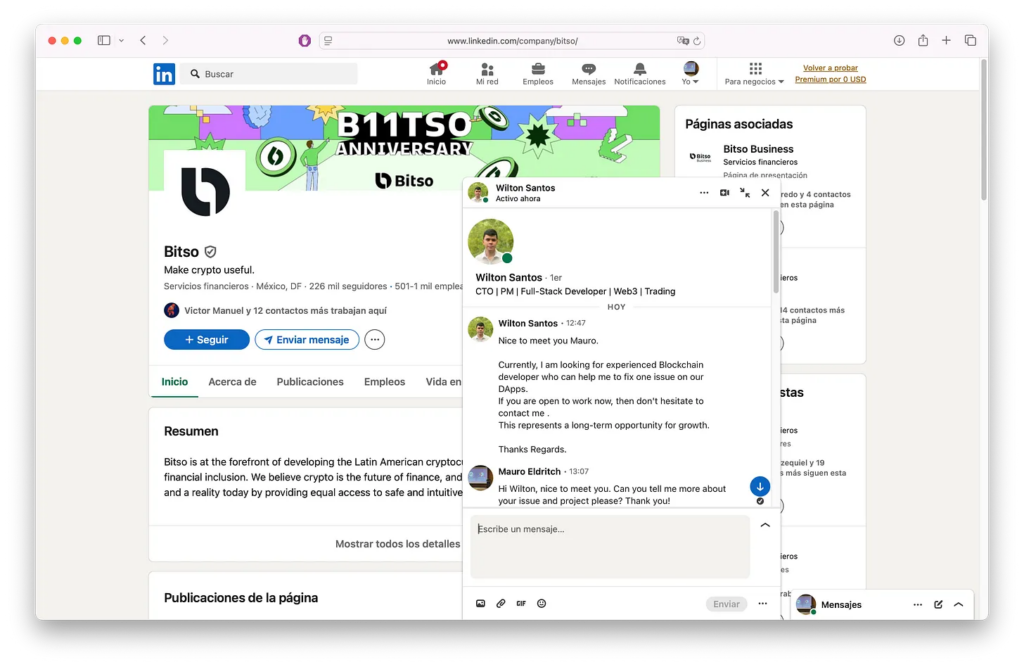
The common losses for victims include stolen cryptocurrency and credentials, compromised systems, and disrupted operations. In some cases, device infections led to downstream supply chain attacks, affecting customers and partners. Crypto and tech firms rely on skilled developers, making them prime targets for social engineering. These attacks disrupt product development, expose proprietary code, and undermine trust in hiring processes, while recovery costs (e.g., system remediation, legal fees) strain budgets.
Hijacking Open Source Packages
Despite doing it since September 2024, Lazarus Group continues to embed malicious backdoors in cloned open-source software packages on repositories like GitHub and PyPI, targeting developers in both medium and large enterprises. Over 230 malicious packages have been identified since the start of 2025, affecting 36,000 firms in Europe, India, and Brazil.
Victims face losses from stolen credentials, authentication tokens, and system data, with recovery costs exceeding millions. Open-source software is critical to tech and crypto industries.
Given that many IT companies work in tight cooperation, a successful attack on an endpoint at one firm can lead to major incidents in other businesses down the supply chain. A notable example here is the $1.5 billion ByBit hack orchestrated by Lazarus.
The initial compromise occurred on a developer’s machine at Safe{Wallet}, a multisignature provider used by ByBit, through a malicious Docker project. From there, the attackers gained access to Safe{Wallet}’s Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 bucket and managed to push a malicious script to the system. This resulted in ByBit’s transaction being hijacked and the funds funneled to a wallet controlled by Lazarus Group.
Current Lazarus Malware Threats and How to Detect Them
Lazarus’s 2025 operations leverage advanced malware and TTPs, tailored to maximize damage to businesses through data theft, system compromise, and financial extortion.
To detect such attacks early, SOC teams require a reliable solution for proactive analysis of suspicious files and URLs. ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox provides a fast, isolated, and hands-on way to expose malware and phishing in seconds.
Let’s take a look at several examples of malware families employed by Lazarus Group in their attacks and see how sandboxing simplifies their identification.
 How Interactive Sandbox boosts SOCs
How Interactive Sandbox boosts SOCs - Higher detection rate with deep insights into threat behavior.
- Shorter MTTR with fast identification of malware and detailed reports for informed mitigation.
- Reduced manual effort with analysis automation.
InvisibleFerret
InvisibleFerret is a modular malware often deployed by Lazarus hackers via fake job interviews, capable of keylogging, screen capturing, and establishing persistent C2 connections to steal sensitive data.
Read technical analysis of InvisibleFerret
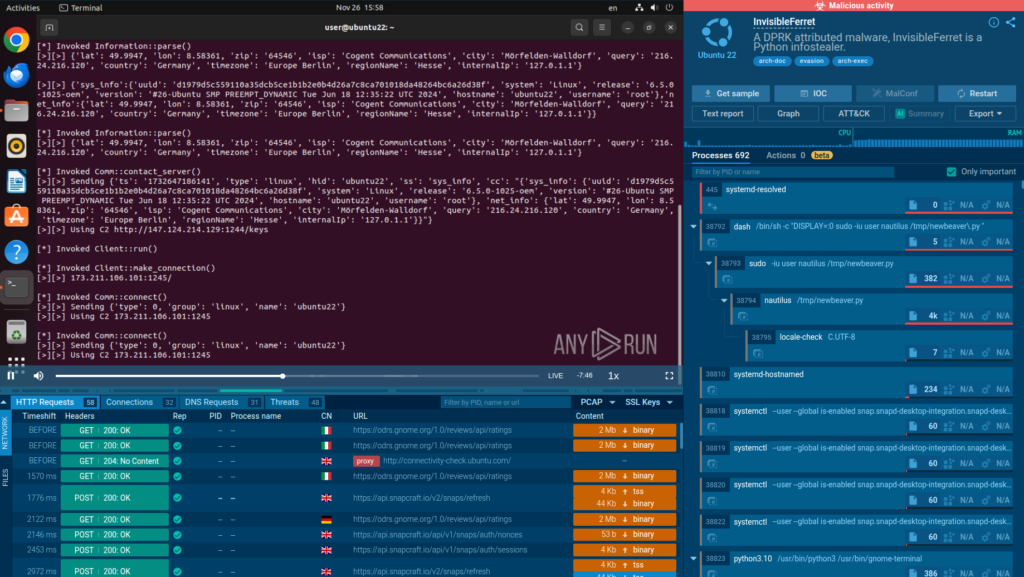
InvisibleFerret compromises developer endpoints, exposing proprietary code and client data.
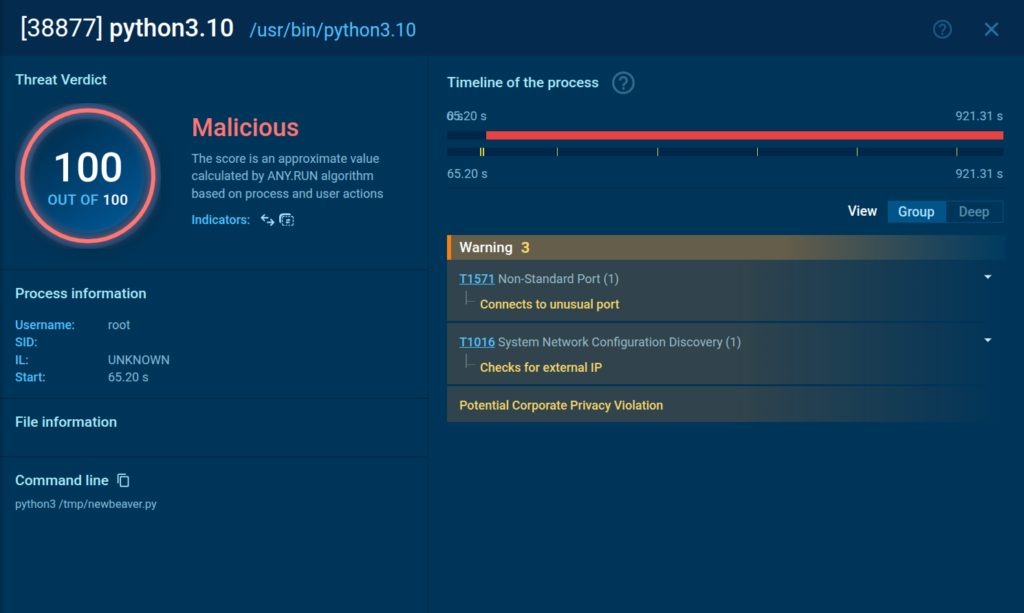
As shown in a sandbox analysis session, the malware engages in several activities on an infected system, such as attempting to connect to an unusual port. In a business setting, armed with this knowledge, SOCs can act proactively and prevent the incident, keeping the network safe.
OtterCookie
OtterCookie is a malware which is often embedded in hijacked open-source packages. It is used as part of the Contagious Interview campaign to extract authentication tokens, session data, and crypto wallets. Stolen tokens allow attackers to bypass authentication, access corporate systems, or customer accounts.
Read technical analysis of OtterCookie
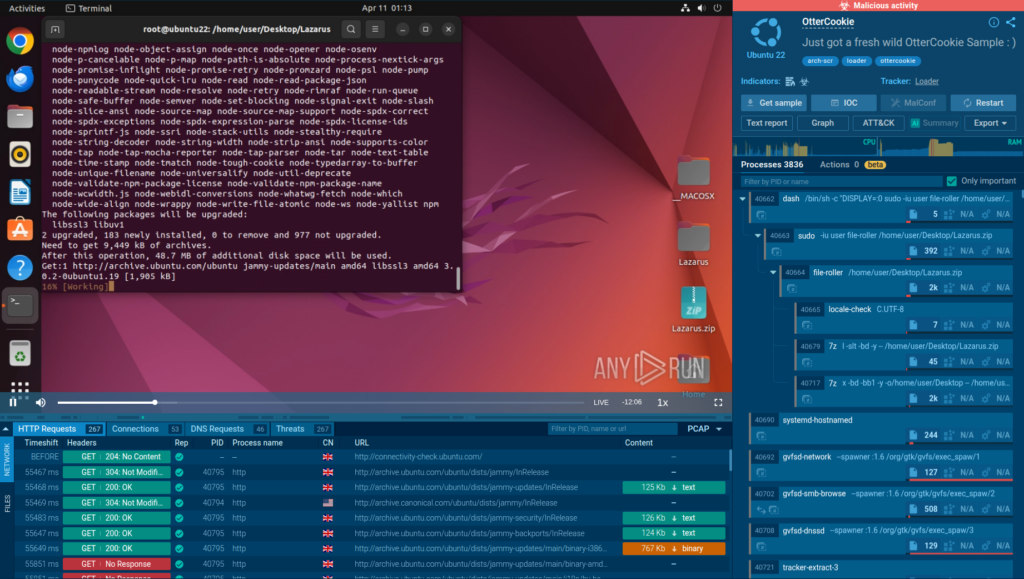
Thanks to the analysis inside ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox, we can observe the entire attack chain for this malware.
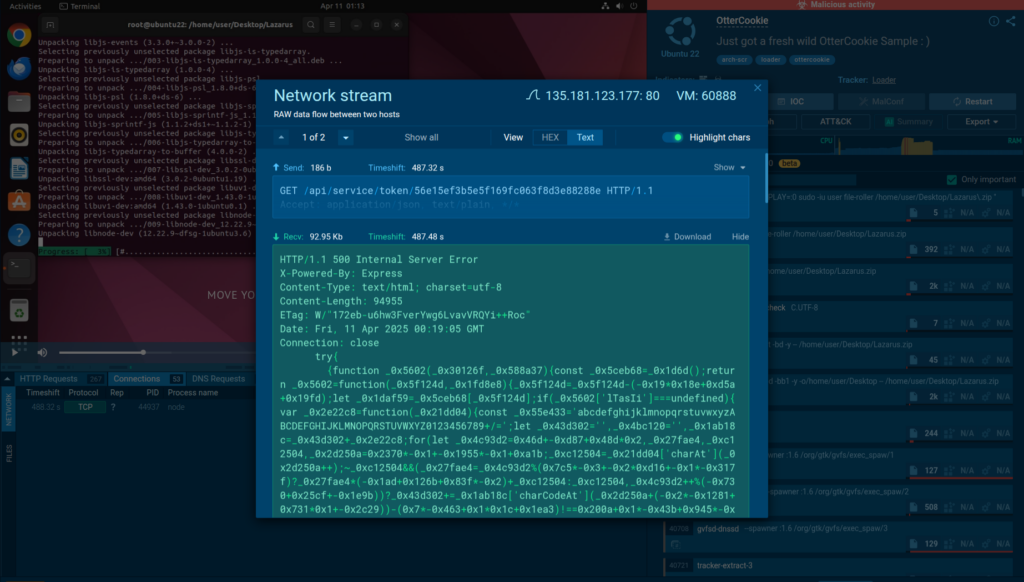
The sandbox session shows that attackers use a fake error and a try/catch block to download and run a piece of malicious code responsible for deploying OtterCookie on the system. This is an evasion technique which may escape detection by signature-based solutions.
With ANY.RUN’s advanced threat tracking, we get notified about the malicious activity and can stop the attack early, keeping our company’s infrastructure secure and free from disruptions.
PyLangGhost RAT
PyLangGhost is a relatively new remote access trojan from Lazarus APT. Delivered via fake interviews or malicious packages, it enables long-term espionage and data theft, compromising trade secrets and customer data. As a result of its activities, businesses may face prolonged downtime during remediation and regulatory fines for data breaches.
Read technical analysis of OtterCookie
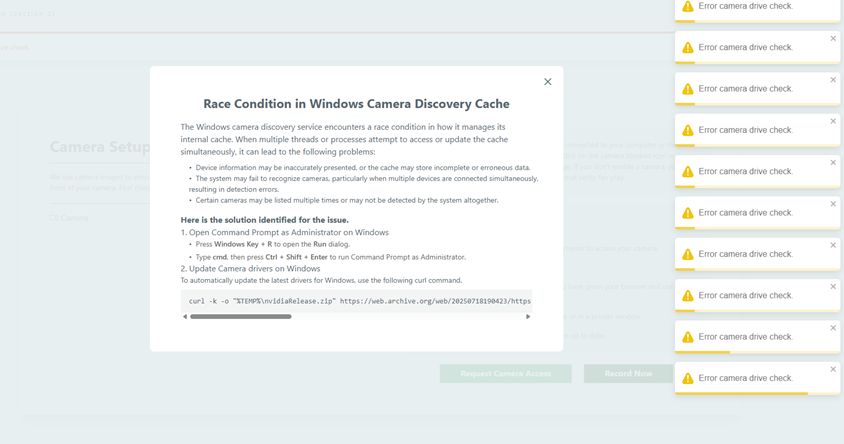
The malware has been observed in attacks involving the use of the ClickFix tactic, a trick that presents victims with a fake page instructing them to run a malicious script on their system as a way to solve an error or verify their identity.
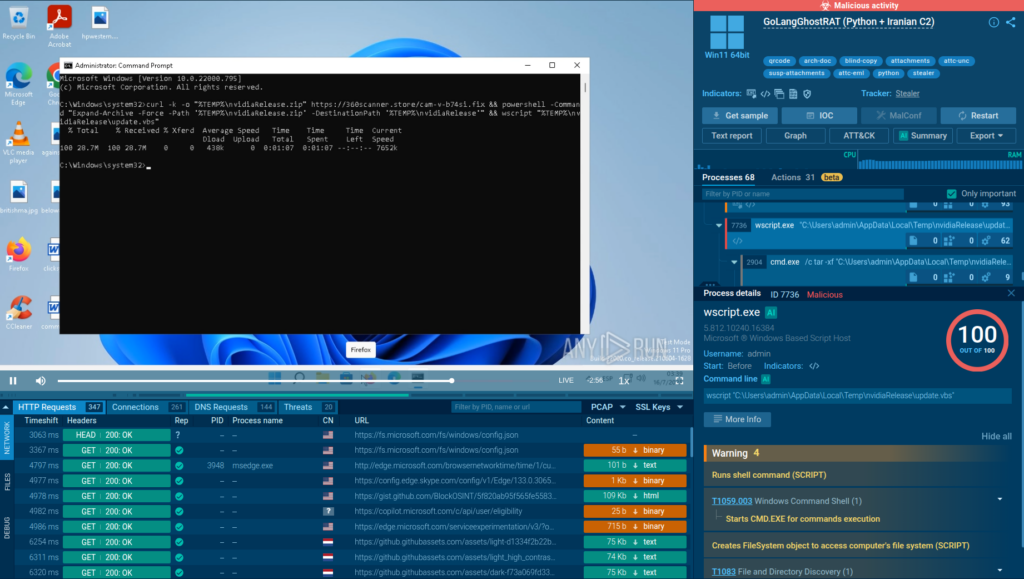
In the case of PyLangGhost, users were often asked to paste and run a command on their computer to fix an issue with their camera. Using the interactivity of ANY.RUN’s sandbox, we can manually perform these actions in an isolated, cloud-based virtual environment to trigger the threat’s execution. The result is a malware being installed on the system, as you can see in the analysis.
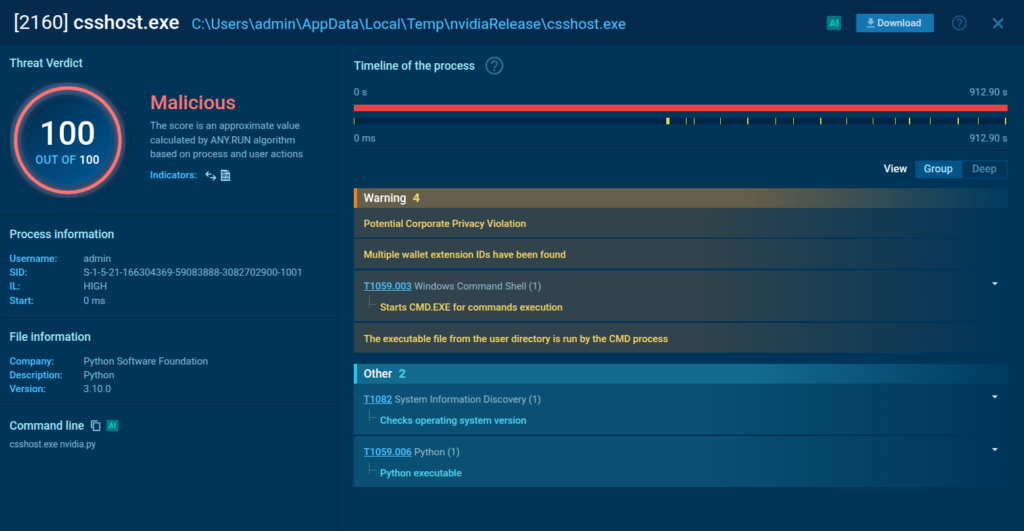
The sandbox marks the processes spawned by the threat as malicious, providing analysts with a definitive and actionable verdict for instant incident resolution.
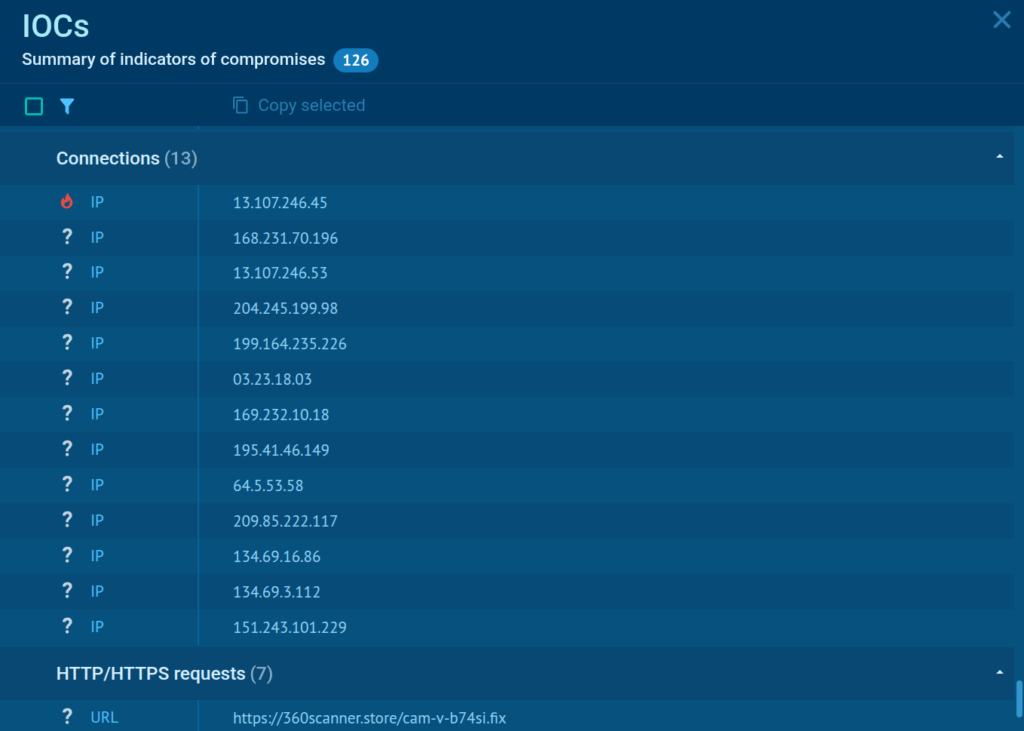
Once the investigation is over, we can collect the indicators of compromise (IOCs) gathered by ANY.RUN and use them to create detection rules to spot future attacks in advance.
How to Identify and Track Lazarus Attacks with Threat Intelligence
To keep up with the evolution of Lazarus Group’s attacks, we can utilize ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup. It is a free-access database of the latest indicators of compromise, behavior (IOBs), and attack (IOAs). This data is extracted from live sandbox analyses of active malware and phishing attacks across 15,000 SOCs, ensuring the indicators are fresh and available quickly after an attack.
To see examples of Lazarus Group’s recent attacks, we can start with a simple query:
threatName:”lazarus”
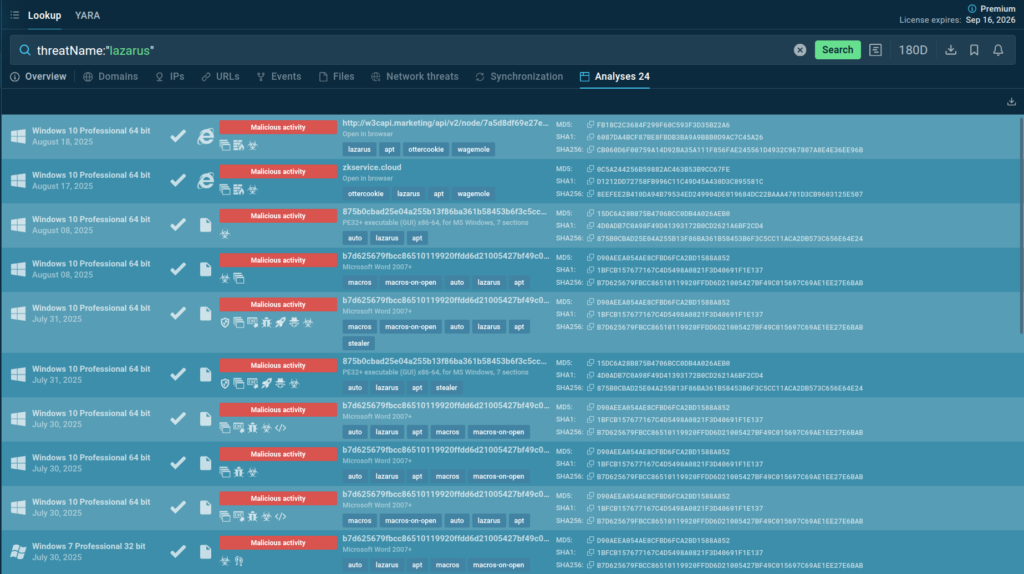
The service provides us with a list of sandbox sessions with threats attributed to the Lazarus APT. This provides us with rich context about the current malware families, TTPs, and campaigns run by the group. For example, as visible from a report from August 17, the OtterCookie malware is still in use.
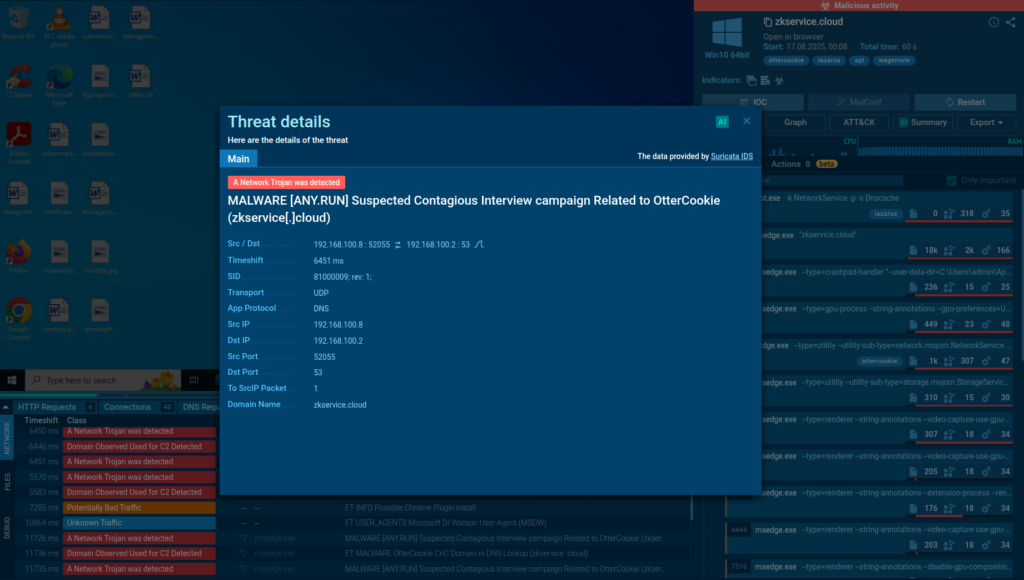
We can dive deeper into each report to collect actionable indicators for detection rules and see what threats the North Korean hackers are using right now.
With TI Lookup, SOC teams can:
- Accelerated Response: Reduce MTTR by quickly understanding threat behavior, objectives, and targets through sandbox analysis.
- Enriched Threat Investigations: Gain deeper insight into threats by connecting existing artifacts with real-world attacks.
- Stronger Proactive Defense: Gather intelligence on emerging threats to act before they cause damage.
- Improved Detection Rules: Leverage intelligence from TI Lookup to refine SIEM, IDS/IPS, and EDR rules for stronger proactive defense.
About ANY.RUN
Over 500,000 cybersecurity professionals and 15,000+ companies in finance, manufacturing, healthcare, and other sectors rely on ANY.RUN to streamline malware investigations worldwide.
Speed up triage and response by detonating suspicious files in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox, observing malicious behavior in real time, and gathering insights for faster, more confident security decisions. Paired with Threat Intelligence Lookup and Threat Intelligence Feeds, it provides actionable data on cyberattacks to improve detection and deepen your understanding of evolving threats.
Explore more ANY.RUN’s capabilities during 14-day trial→
The post Lazarus Group Attacks in 2025: Here’s Everything SOC Teams Need to Know appeared first on ANY.RUN’s Cybersecurity Blog.
ANY.RUN’s Cybersecurity Blog – Read More
