Pangea Launches AI Guard and Prompt Guard to Combat Gen-AI Security Risks
Guardrail specialist releases new products to aid the development and use of secure gen-AI apps.
The post Pangea Launches AI Guard and Prompt Guard to Combat Gen-AI Security Risks appeared first on SecurityWeek.
SecurityWeek – Read More
VC giant Insight Partners confirms January cyberattack
The VC firm has $90 billion in assets under management and invested in several unicorn cybersecurity startups
© 2024 TechCrunch. All rights reserved. For personal use only.
Security News | TechCrunch – Read More
How Phished Data Turns into Apple & Google Wallets
Carding — the underground business of stealing, selling and swiping stolen payment card data — has long been the dominion of Russia-based hackers. Happily, the broad deployment of more secure chip-based payment cards in the United States has weakened the carding market. But a flurry of innovation from cybercrime groups in China is breathing new life into the carding industry, by turning phished card data into mobile wallets that can be used online and at main street stores.
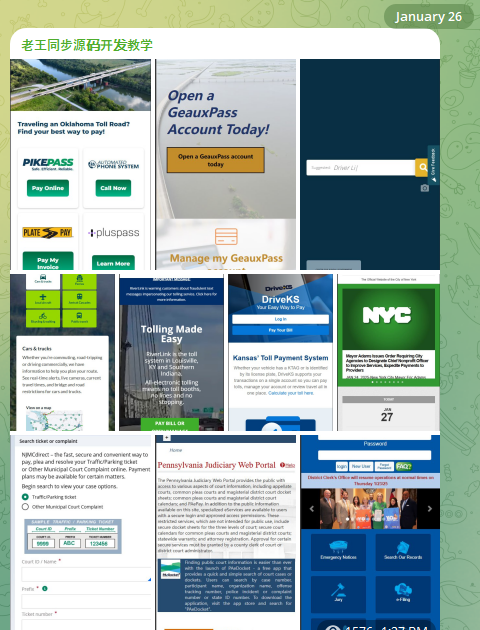
An image from one Chinese phishing group’s Telegram channel shows various toll road phish kits available.
If you own a mobile phone, the chances are excellent that at some point in the past two years it has received at least one phishing message that spoofs the U.S. Postal Service to supposedly collect some outstanding delivery fee, or an SMS that pretends to be a local toll road operator warning of a delinquent toll fee.
These messages are being sent through sophisticated phishing kits sold by several cybercriminals based in mainland China. And they are not traditional SMS phishing or “smishing” messages, as they bypass the mobile networks entirely. Rather, the missives are sent through the Apple iMessage service and through RCS, the functionally equivalent technology on Google phones.
People who enter their payment card data at one of these sites will be told their financial institution needs to verify the small transaction by sending a one-time passcode to the customer’s mobile device. In reality, that code will be sent by the victim’s financial institution to verify that the user indeed wishes to link their card information to a mobile wallet.
If the victim then provides that one-time code, the phishers will link the card data to a new mobile wallet from Apple or Google, loading the wallet onto a mobile phone that the scammers control.
CARDING REINVENTED
Ford Merrill works in security research at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group company. Merrill has been studying the evolution of several China-based smishing gangs, and found that most of them feature helpful and informative video tutorials in their sales accounts on Telegram. Those videos show the thieves are loading multiple stolen digital wallets on a single mobile device, and then selling those phones in bulk for hundreds of dollars apiece.
“Who says carding is dead?,” said Merrill, who presented about his findings at the M3AAWG security conference in Lisbon earlier today. “This is the best mag stripe cloning device ever. This threat actor is saying you need to buy at least 10 phones, and they’ll air ship them to you.”
One promotional video shows stacks of milk crates stuffed full of phones for sale. A closer inspection reveals that each phone is affixed with a handwritten notation that typically references the date its mobile wallets were added, the number of wallets on the device, and the initials of the seller.
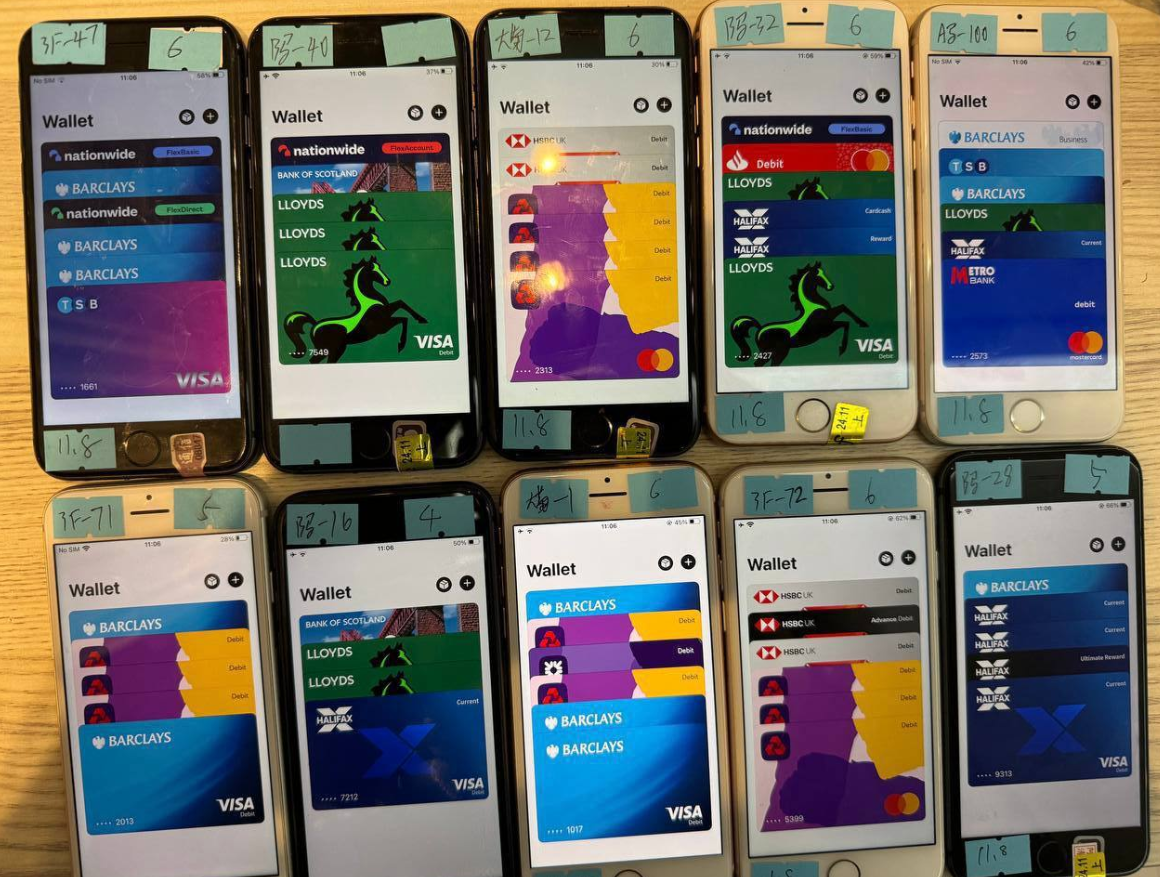
An image from the Telegram channel for a popular Chinese smishing kit vendor shows 10 mobile phones for sale, each loaded with 4-6 digital wallets from different UK financial institutions.
Merrill said one common way criminal groups in China are cashing out with these stolen mobile wallets involves setting up fake e-commerce businesses on Stripe or Zelle and running transactions through those entities — often for amounts totaling between $100 and $500.
Merrill said that when these phishing groups first began operating in earnest two years ago, they would wait between 60 to 90 days before selling the phones or using them for fraud. But these days that waiting period is more like just seven to ten days, he said.
“When they first installed this, the actors were very patient,” he said. “Nowadays, they only wait like 10 days before [the wallets] are hit hard and fast.”
GHOST TAP
Criminals also can cash out mobile wallets by obtaining real point-of-sale terminals and using tap-to-pay on phone after phone. But they also offer a more cutting-edge mobile fraud technology: Merrill found that at least one of the Chinese phishing groups sells an Android app called “ZNFC” that can relay a valid NFC transaction to anywhere in the world. The user simply waves their phone at a local payment terminal that accepts Apple or Google pay, and the app relays an NFC transaction over the Internet from a phone in China.
“The software can work from anywhere in the world,” Merrill said. “These guys provide the software for $500 a month, and it can relay both NFC enabled tap-to-pay as well as any digital wallet. The even have 24-hour support.”
The rise of so-called “ghost tap” mobile software was first documented in November 2024 by security experts at ThreatFabric. Andy Chandler, the company’s chief commercial officer, said their researchers have since identified a number of criminal groups from different regions of the world latching on to this scheme.
Chandler said those include organized crime gangs in Europe that are using similar mobile wallet and NFC attacks to take money out of ATMs made to work with smartphones.
“No one is talking about it, but we’re now seeing ten different methodologies using the same modus operandi, and none of them are doing it the same,” Chandler said. “This is much bigger than the banks are prepared to say.”
A November 2024 story in the Singapore daily The Straits Times reported authorities there arrested three foreign men who were recruited in their home countries via social messaging platforms, and given ghost tap apps with which to purchase expensive items from retailers, including mobile phones, jewelry, and gold bars.
“Since Nov 4, at least 10 victims who had fallen for e-commerce scams have reported unauthorised transactions totaling more than $100,000 on their credit cards for purchases such as electronic products, like iPhones and chargers, and jewelry in Singapore,” The Straits Times wrote, noting that in another case with a similar modus operandi, the police arrested a Malaysian man and woman on Nov 8.
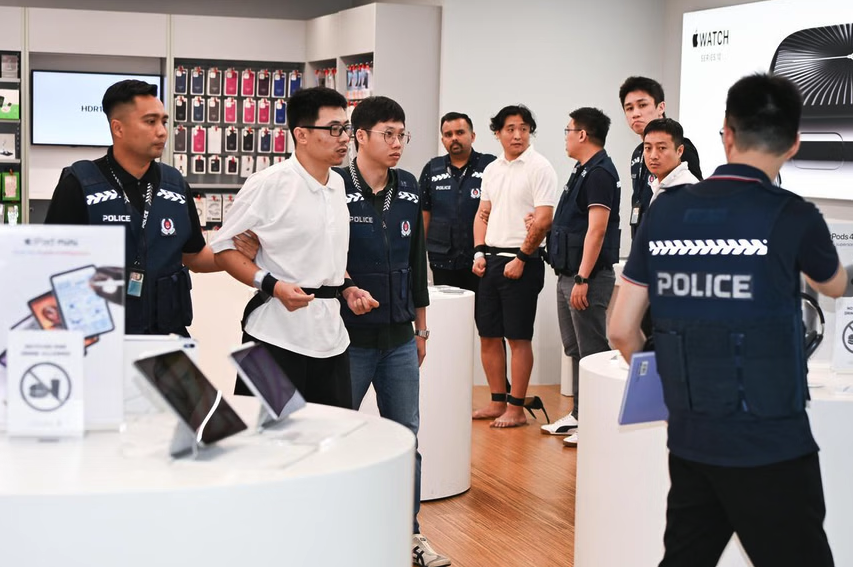

Three individuals charged with using ghost tap software at an electronics store in Singapore. Image: The Straits Times.
ADVANCED PHISHING TECHNIQUES
According to Merrill, the phishing pages that spoof the USPS and various toll road operators are powered by several innovations designed to maximize the extraction of victim data.
For example, a would-be smishing victim might enter their personal and financial information, but then decide the whole thing is scam before actually submitting the data. In this case, anything typed into the data fields of the phishing page will be captured in real time, regardless of whether the visitor actually clicks the “submit” button.
Merrill said people who submit payment card data to these phishing sites often are then told their card can’t be processed, and urged to use a different card. This technique, he said, sometimes allows the phishers to steal more than one mobile wallet per victim.
Many phishing websites expose victim data by storing the stolen information directly on the phishing domain. But Merrill said these Chinese phishing kits will forward all victim data to a back-end database operated by the phishing kit vendors. That way, even when the smishing sites get taken down for fraud, the stolen data is still safe and secure.
Another important innovation is the use of mass-created Apple and Google user accounts through which these phishers send their spam messages. One of the Chinese phishing groups posted images on their Telegram sales channels showing how these robot Apple and Google accounts are loaded onto Apple and Google phones, and arranged snugly next to each other in an expansive, multi-tiered rack that sits directly in front of the phishing service operator.
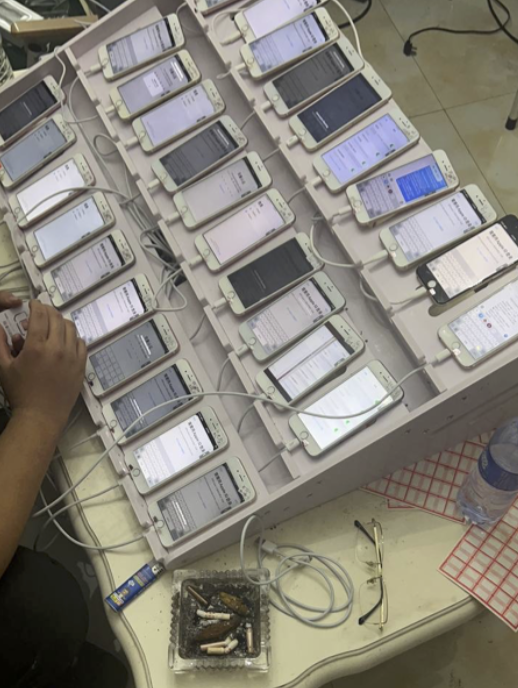

The ashtray says: You’ve been phishing all night.
In other words, the smishing websites are powered by real human operators as long as new messages are being sent. Merrill said the criminals appear to send only a few dozen messages at a time, likely because completing the scam takes manual work by the human operators in China. After all, most one-time codes used for mobile wallet provisioning are generally only good for a few minutes before they expire.
Notably, none of the phishing sites spoofing the toll operators or postal services will load in a regular Web browser; they will only render if they detect that a visitor is coming from a mobile device.
“One of the reasons they want you to be on a mobile device is they want you to be on the same device that is going to receive the one-time code,” Merrill said. “They also want to minimize the chances you will leave. And if they want to get that mobile tokenization and grab your one-time code, they need a live operator.”
Merrill found the Chinese phishing kits feature another innovation that makes it simple for customers to turn stolen card details into a mobile wallet: They programmatically take the card data supplied by the phishing victim and convert it into a digital image of a real payment card that matches that victim’s financial institution. That way, attempting to enroll a stolen card into Apple Pay, for example, becomes as easy as scanning the fabricated card image with an iPhone.
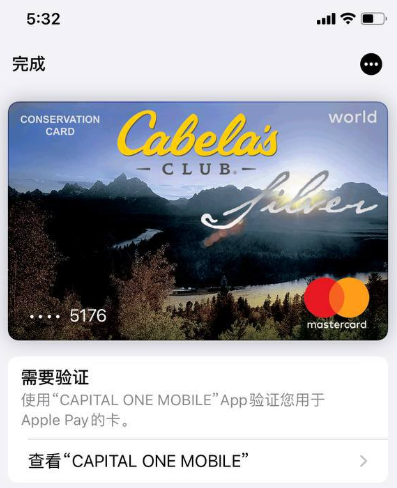
An ad from a Chinese SMS phishing group’s Telegram channel showing how the service converts stolen card data into an image of the stolen card.
“The phone isn’t smart enough to know whether it’s a real card or just an image,” Merrill said. “So it scans the card into Apple Pay, which says okay we need to verify that you’re the owner of the card by sending a one-time code.”
PROFITS
How profitable are these mobile phishing kits? The best guess so far comes from data gathered by other security researchers who’ve been tracking these advanced Chinese phishing vendors.
In August 2023, the security firm Resecurity discovered a vulnerability in one popular Chinese phish kit vendor’s platform that exposed the personal and financial data of phishing victims. Resecurity dubbed the group the Smishing Triad, and found the gang had harvested 108,044 payment cards across 31 phishing domains (3,485 cards per domain).
In August 2024, security researcher Grant Smith gave a presentation at the DEFCON security conference about tracking down the Smishing Triad after scammers spoofing the U.S. Postal Service duped his wife. By identifying a different vulnerability in the gang’s phishing kit, Smith said he was able to see that people entered 438,669 unique credit cards in 1,133 phishing domains (387 cards per domain).
Based on his research, Merrill said it’s reasonable to expect between $100 and $500 in losses on each card that is turned into a mobile wallet. Merrill said they observed nearly 33,000 unique domains tied to these Chinese smishing groups during the year between the publication of Resecurity’s research and Smith’s DEFCON talk.
Using a median number of 1,935 cards per domain and a conservative loss of $250 per card, that comes out to about $15 billion in fraudulent charges over a year.
Merrill was reluctant to say whether he’d identified additional security vulnerabilities in any of the phishing kits sold by the Chinese groups, noting that the phishers quickly fixed the vulnerabilities that were detailed publicly by Resecurity and Smith.
FIGHTING BACK
Adoption of touchless payments took off in the United States after the Coronavirus pandemic emerged, and many financial institutions in the United States were eager to make it simple for customers to link payment cards to mobile wallets. Thus, the authentication requirement for doing so defaulted to sending the customer a one-time code via SMS.
Experts say the continued reliance on one-time codes for onboarding mobile wallets has fostered this new wave of carding. KrebsOnSecurity interviewed a security executive from a large European financial institution who spoke on condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak to the press.
That expert said the lag between the phishing of victim card data and its eventual use for fraud has left many financial institutions struggling to correlate the causes of their losses.
“That’s part of why the industry as a whole has been caught by surprise,” the expert said. “A lot of people are asking, how this is possible now that we’ve tokenized a plaintext process. We’ve never seen the volume of sending and people responding that we’re seeing with these phishers.”
To improve the security of digital wallet provisioning, some banks in Europe and Asia require customers to log in to the bank’s mobile app before they can link a digital wallet to their device.
Addressing the ghost tap threat may require updates to contactless payment terminals, to better identify NFC transactions that are being relayed from another device. But experts say it’s unrealistic to expect retailers will be eager to replace existing payment terminals before their expected lifespans expire.
And of course Apple and Google have an increased role to play as well, given that their accounts are being created en masse and used to blast out these smishing messages. Both companies could easily tell which of their devices suddenly have 7-10 different mobile wallets added from 7-10 different people around the world. They could also recommend that financial institutions use more secure authentication methods for mobile wallet provisioning.
Neither Apple nor Google responded to requests for comment on this story.
Krebs on Security – Read More
Ecuador’s legislature says hackers attempted to access confidential information
The National Assembly, Ecuador’s unicameral legislature, says it was able to “identify and counteract” attempts by malicious hackers to breach sensitive systems.
The Record from Recorded Future News – Read More
Critical OpenSSH Vulnerabilities Expose Users to MITM and DoS Attacks
Two critical OpenSSH vulnerabilities discovered! Qualys TRU finds client and server flaws (CVE-2025-26465 & CVE-2025-26466) enabling MITM and…
Hackread – Latest Cybersecurity, Tech, AI, Crypto & Hacking News – Read More
Why rebooting your phone daily is your best defense against zero-click attacks
Phone hacking technologies are becoming more and more inconspicuous. That’s why you should treat your phone like a computer, according to this cybersecurity expert.
Latest stories for ZDNET in Security – Read More
Cyberattack likely to have ‘material impact’ on media giant Lee Enterprises’ bottom line
Media conglomerate Lee Enterprises told regulators on Friday that hackers had stolen files and encrypted “critical applications” as part of an incident that impacted the operations of dozens of newspapers nationwide.
The Record from Recorded Future News – Read More
Snake Keylogger Variant Hits Windows, Steals Data via Telegram Bots
The New Snake Keylogger variant targets Windows users via phishing emails, using AutoIt for stealth. Learn how it…
Hackread – Latest Cybersecurity, Tech, AI, Crypto & Hacking News – Read More
MirrorTab Raises $8.5M Seed Round to Take on Browser-Based Attacks
San Francisco startup secures $8.5 million in seed funding led by Valley Capital Partners to tackle browser-based malware attacks.
The post MirrorTab Raises $8.5M Seed Round to Take on Browser-Based Attacks appeared first on SecurityWeek.
SecurityWeek – Read More

